
Alonso de Ojeda y su aventura americana YouTube
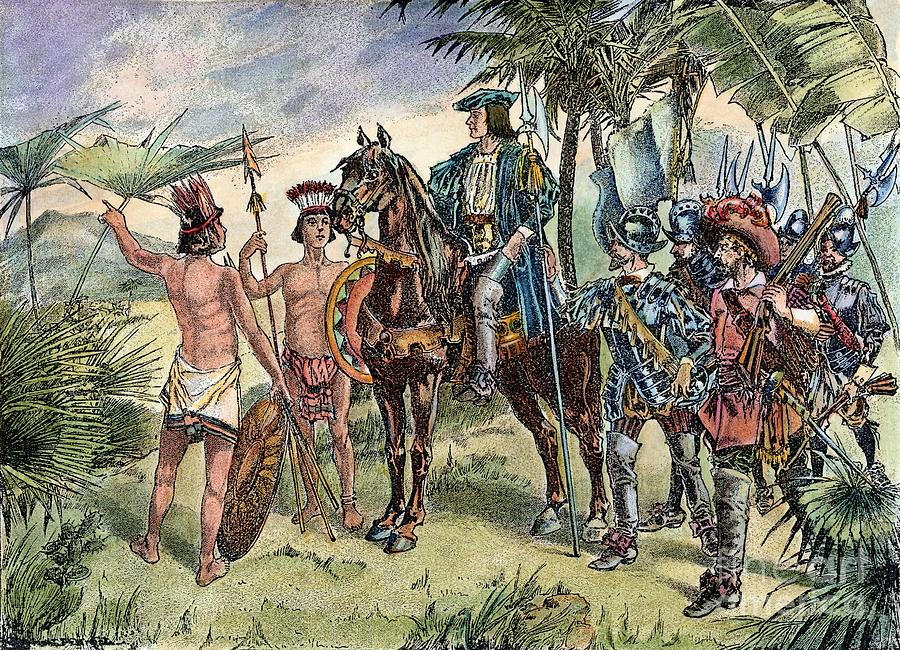
Balboa In Vasco Núñez de Balboa: Career in the New World.to a colony founded by Alonso de Ojeda on the coast of Urabá, in modern Colombia. The expedition found the survivors of the colony, led by Francisco Pizarro, but Ojeda had departed. On the advice of Balboa the settlers moved across the Gulf of Urabá to Darién, on the less… Read More Columbus

antiguo libro alonso de hojeda grandezas es Comprar Libros antiguos biografías en
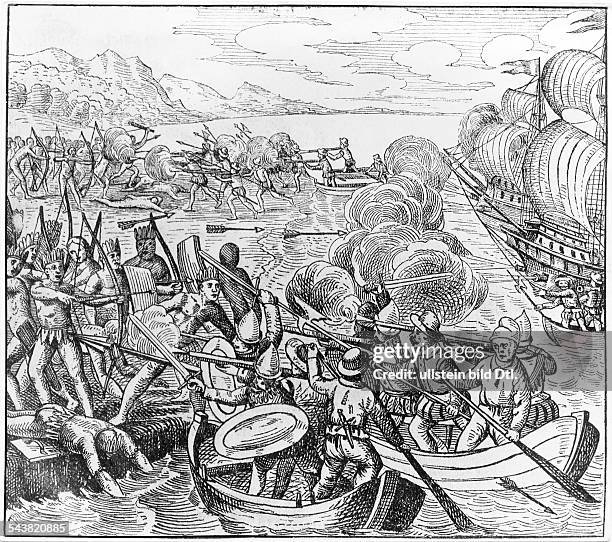
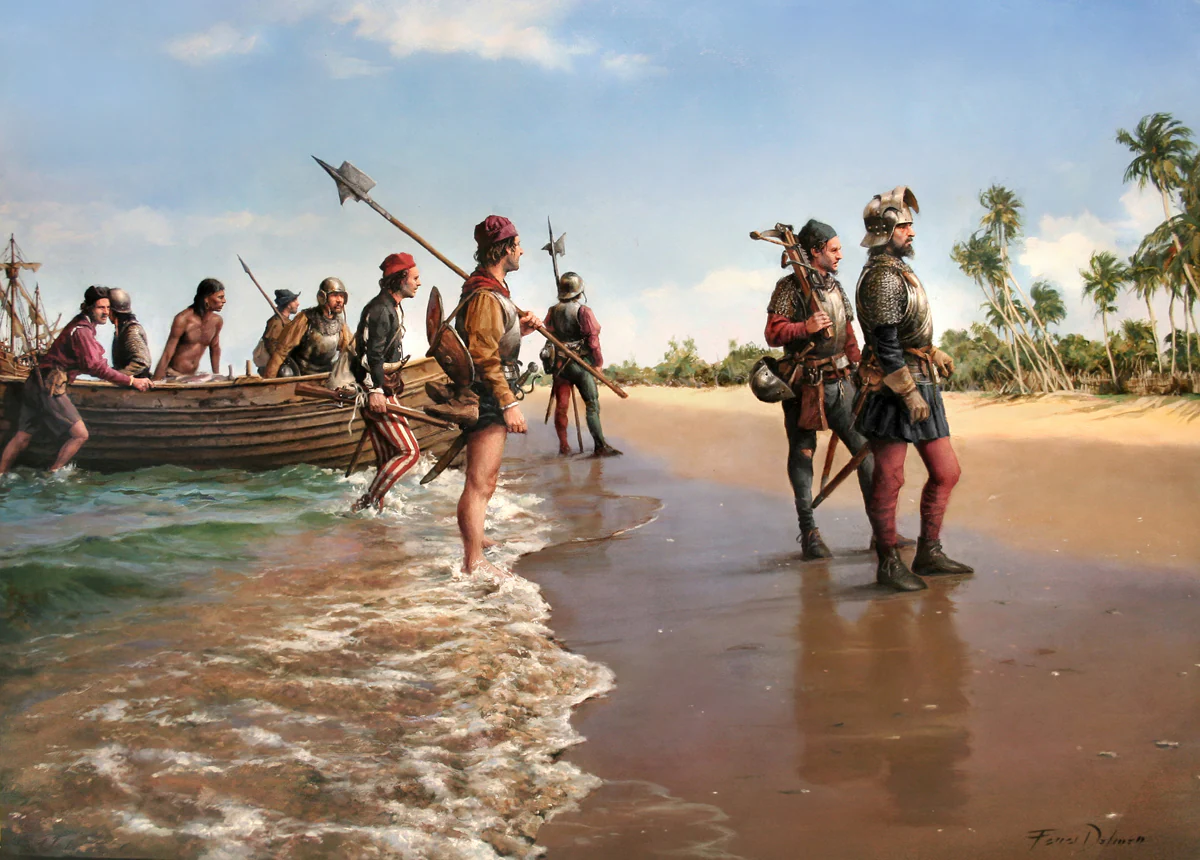
Alonso de Ojeda and his associates left. The route taken by this expedition, after leaving the African coast of Cape Verde to cross the Atlantic, reached American coasts a little further south than Columbus on his third voyage, near the mouth of the river Esequibo. From there they took a southerly course but faced with the difficulties of.

1499 Los viajes Alonso de Ojeda (1499,1502, 1509). la Historia sin Historietas
In 1477 a preacher named Alonso de Hojeda warned King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella of Spain that heretics were undermining the Christian Church in their kingdoms and something had to be done. In 1478, Pope Sixtus IV gave the monarchs the right to name inquisitors, and in 1480, the first inquisitors named by the monarchs began their work.

Hojeda Photos and Premium High Res Pictures Getty Images
Alonso De Ojeda. English: Alonso de Ojeda (c.1468) - 1515) — a Spanish navigator on the second voyage of Columbus, a conquistador, and a colonial governor. He travelled through present day Trinidad and Tobago, Curaçao, Aruba, Guyana, Venezuela, and Colombia. Ojeda named Venezuela, when establishing the Governorate of New Andalusia (1501.
Alonso de Ojeda biografía, viajes, ciudades fundadas, muerte
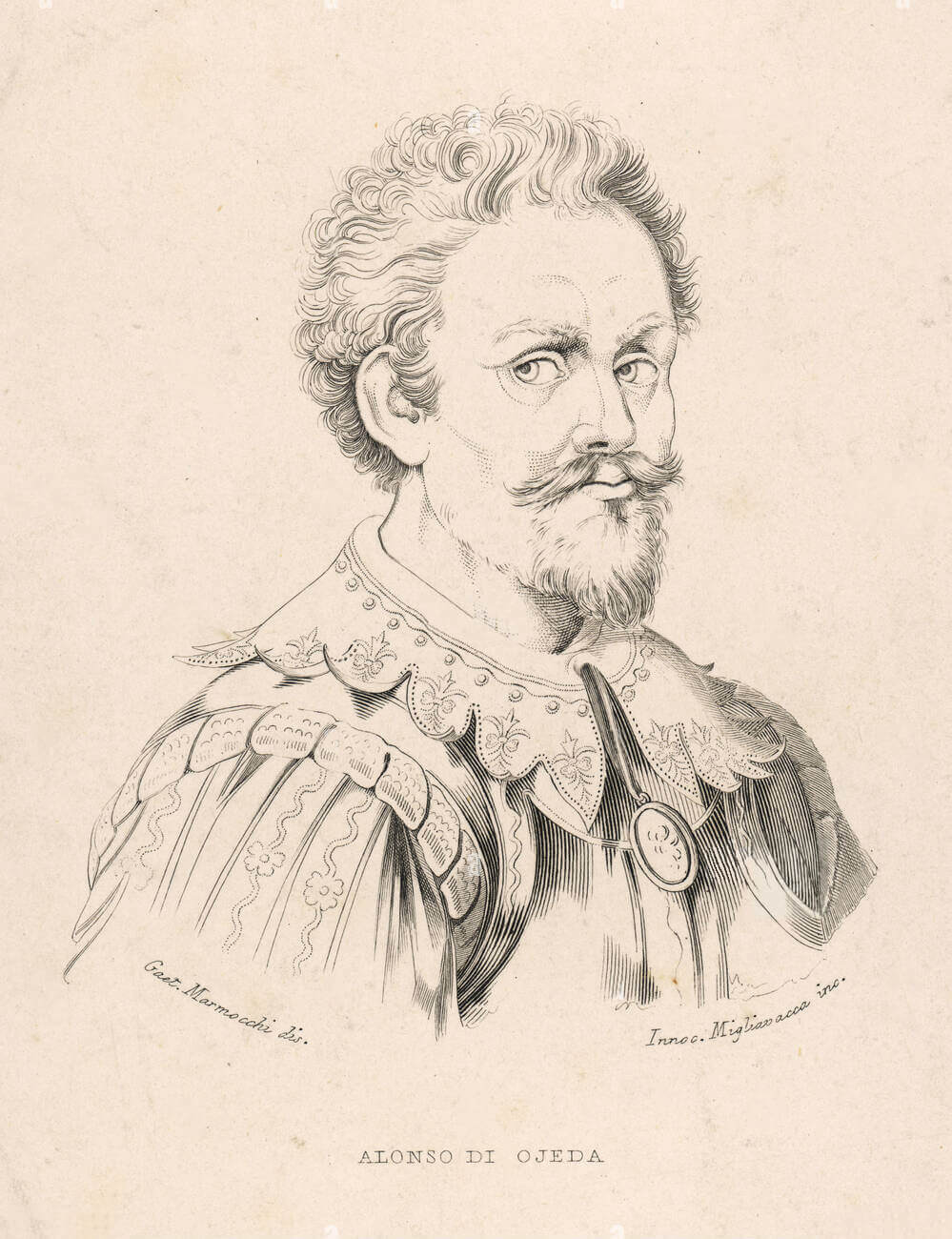
Alonso de Ojeda ( Spanish pronunciation: [aˈlonso ðe oˈxeða]; c. 1466 - c. 1515) was a Spanish explorer, governor and conquistador. He travelled through modern-day Guyana, Venezuela, Trinidad, Tobago, Curaçao, Aruba and Colombia, at times with Amerigo Vespucci and Juan de la Cosa.

CVC. Cuenca. Alonso de Ojeda.
Alonso de Ojeda (älōn´sō ŧħā ōhā´ŧħä), c.1466-1515?, Spanish conquistador.He joined Columbus on his second voyage and in 1499—at first accompanied by Vespucci—explored the northeastern coast of South America.In 1508 he was made governor of territories of N South America.Near present Cartagena he was defeated by the Native Americans and virtually rescued by Diego de Nicuesa.

ALONSO de OJEDA Photograph by Granger
Alonso de Ojeda ( Torrejoncillo del Rey; 1468 - Santo Domingo; 1515) fue un navegante, gobernador y conquistador español; recorrió las costas que luego serían Colombia, Guyana, Trinidad, Tobago, Curazao, Aruba y Venezuela.

Historia y biografía de Alonso de Ojeda
Alonso de Ojeda. Ojeda, Alonso de. Moguer (Huelva), f. s. xv - Honduras, s. xvi. Conquistador, encomendero. Según cuenta Las Casas, en 1511 participó en la conquista de Cuba. También algunas informaciones aseguran que estuvo en las expediciones de Fernández de Córdoba y de Juan de Grijalva al Yucatán. Posteriormente se unió a la hueste.

Alonso de Ojeda La Venciclopedia
At first, the activity of the Inquisition was limited to the dioceses of Seville and Cordoba, where Alonso de Hojeda had detected converso activity. The first Auto de Fé was celebrated in Seville on February 6, 1481: six people were burned alive. Alonso de Hojeda himself gave the sermon. The Inquisition then grew rapidly.

Antiguo libro alonso de hojeda grandezas es Vendido en Venta Directa 41833145
Alonso de Hojeda (także Alonso de Ojeda, ur. 1468 w Cuenca, Hiszpania zm. 1515 w Santo Domingo, Dominikana) - hiszpański żeglarz, gubernator i konkwistador, badacz wybrzeży Gujany, Wenezueli, Kolumbii i wysp Indii Zachodnich. Europejski odkrywca Jeziora Maracaibo . Wczesne życie

Salamanca Activa NÚÑEZ DE BALBOA (PARTE II)
Explorer; b. at Cuenca, Spain, about 1466; d. on the island of Santo Domingo, about 1508. He came of an impoverished noble family, but had the good fortune to start his career in the household of the Dukes of Medina Sidonia. He early gained the patronage of Juan Rodríguez de Fonseca, Bishop of Burgos and later Patriarch of the Indies, who made.

El primer conquistador español Alonso de ojeda YouTube
Alonso de Ojeda Ojeda, Alonso de. Torrejoncillo del Rey (Cuenca), 1466-1470 - Santo Domingo (República Dominicana), 1516. Explorador, conquistador, gobernador de Nueva Andalucía. Nació en Torrejoncillo del Rey, entonces conocido como Torrejoncillo de Huete, en una fecha indeterminada cuyo arco varía, según los autores, entre 1466 y 1470.

Las expediciones de Alonso de Ojeda
Alonso de Ojeda is the 70th most popular explorer (down from 64th in 2019), the 243rd most popular biography from Spain (down from 211th in 2019) and the 11th most popular Spanish Explorer. Alonso de Ojeda was a Spanish explorer and conquistador who led the first European expedition to explore the northern coast of South America. He was one of.

Brasil ficou 'mal acostumado' a ter muitos pilotos na F1, diz Alonso GQ Motor
Alonso de Ojeda. 1466-1510. Spanish explorer who participated in the early exploration and conquest of America by Spain. He accompanied Christopher Columbus on his second American voyage in 1493, and in 1496 he brought natives back to Spain as slaves from another voyage of exploration. In 1502 and 1510, his attempts to establish colonies in America failed.

Fototeca Gilardi > Foto FTT43630 AMERIGO VESPUCCI
Alonso de Ojeda ( b. ca. 1466; d. 1516), Spanish navigator and conquistador. Ojeda traveled with Christopher Columbus on his second voyage in 1493 and partook in explorations of Guadalupe and Hispaniola. Years later he obtained permission to travel to the mainland following the route of Columbus's third voyage.

antiguo libro alonso de hojeda grandezas es Comprar Libros antiguos biografías en
La exploración de Venezuela Alonso de Ojeda estuvo en la Española hasta fines de 1498, momento en que se enemistó con Colón y regresó a España. Fue a la Corte y se entrevistó con el Obispo Fonseca, que le pidió comprobar lo descubierto por Colón en su tercer viaje; se le autorizó así a realizar el primer viaje de descubrimiento tras los colombinos.