
Portrait of Florence Nightingale Collection
Updated on July 21, 2019. Florence Nightingale (May 12, 1820-August 13, 1910), a nurse and social reformer, is considered the founder of the modern nursing profession who helped promote medical training and raise hygiene standards. She served as head nurse for the British during the Crimean War, where she was known as "The Lady With the Lamp.

Florence Nightingale Libraries
Named after the city of her birth, Nightingale was born at the Villa Colombia in Florence, Italy, on 12 May 1820. Her parents, William Edward Nightingale and his wife Frances Smith, were touring Europe for the first two years of their marriage. Nightingale's elder sister had been born in Naples the year before.

Florence Nightingale 18201910 St Margaret of Antioch
Born on May 12, 1820, Nightingale was smart and observant. At her first job in the early 1850s, caring for sick teachers in London, England, she became superintendent after quickly showing her talent for helping the sick get better. It was also when she developed ideas that would change healthcare forever. The mostly male doctors of the day.

English nursing reformer Florence Nightingale , who became the first... Nachrichtenfoto Getty
Florence Nightingale (1820 - 1910) Volunteered to nurse soldiers during the Crimean War. Nightingale's analysis of mortality rates helped to improve hospital practices. She also helped improve the standard and prestige of the nursing profession. She is considered to be the founder of modern nursing.

Florence Nightingale Biography YouTube
Florence Nightingale was born on May 12, 1820, in Florence, Italy. Although her parents were from England, she was born in Italy while they were traveling. Both Florence and her older sister Parthenope were named after the Italian cities where they were born. When they returned to England in 1821, the Nightingale family lived in two homes.

Florence Nightingale on what makes a good nurse OpenLearn Open University
Florence Nightingale OM RRC DStJ (/ ˈ n aɪ t ɪ ŋ ɡ eɪ l /; 12 May 1820 - 13 August 1910) was an English social reformer, statistician and the founder of modern nursing.Nightingale came to prominence while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses during the Crimean War, in which she organised care for wounded soldiers at Constantinople. She significantly reduced death rates by.

Florence Nightingale Biography Facts, Childhood, Family Life & Achievements
Florence Nightingale, (born May 12, 1820, Florence, Italy—died Aug. 13, 1910, London, Eng.), Italian-born British nurse, founder of trained nursing as a profession.As a volunteer nurse, she was put in charge of nursing the military in Turkey during the Crimean War.Her first concern was sanitation: patients' quarters were infested with rats and fleas, and the water allowance was one pint.

Florence Nightingale Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help
Florence Nightingale was a British nurse, social reformer, and statistician who is also credited as the founder of modern nursing. She was born on May 12, 1820, in Florence, Italy where her parents were vacationing. The second daughter to William and Frances Nightingale, Florence was raised in a wealthy English family with many social ties to.

Florence Nightingale English Social Reformer, Statistician
Introduction. Florence Nightingale was a Victorian-era English woman who greatly improved the care. of sick and dying soldiers during the Crimean war. She was the lady carrying a lamp as she. made her way through the dark and damp halls of a make-shift hospital where hundreds of. men lay inches apart in unspeakable conditions.

The Life and Legacy of Florence Nightingale The Historic England Blog
Florence Nightingale (1820-1910), known as "The Lady With the Lamp," was a British nurse, social reformer and statistician best known as the founder of modern nursing. Her experiences as a.

Florence Nightingale la precursora de la enfermería moderna Plumas Atómicas
Florence Nightingale is the most recognized name in the field of nursing. Her work was instrumental for developing modern nursing practice, and from her first shift, she worked to ensure patients in her care had what they needed to get healthy. Her Environmental Theory changed the face of nursing to create sanitary conditions for patients to get care.
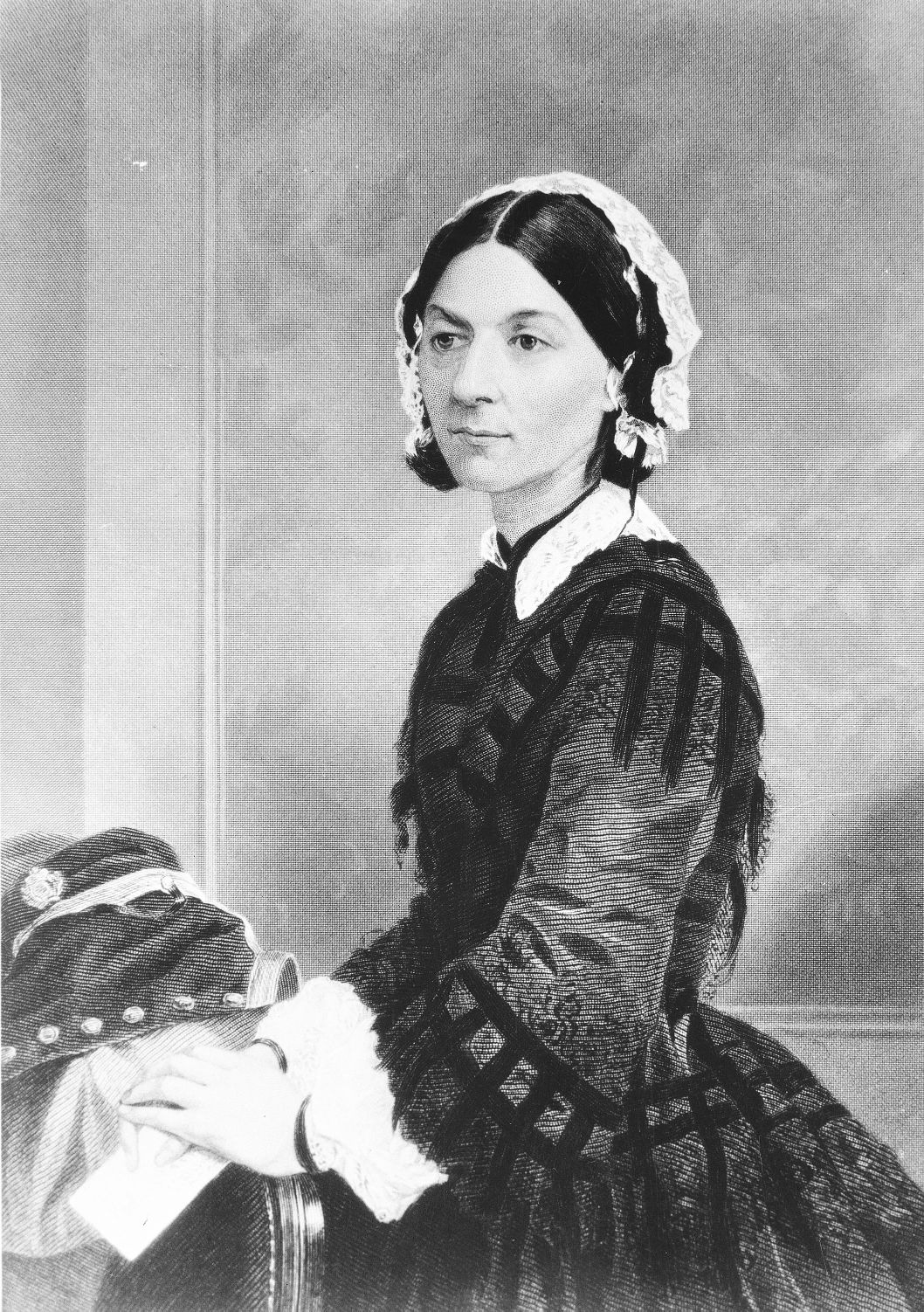
Today In History, Aug. 13 Florence Nightingale History
Florence Nightingale Biography (Social Reformer & Founder of Modern Nursing and Known as 'The Lady with the Lamp') Birthday: May 12, 1820 . Born In: Florence, Italy. Advanced Search. Florence Nightingale was a British social reformer who founded modern nursing. Her biggest contribution to humanity was when she volunteered to help in the Crimean.
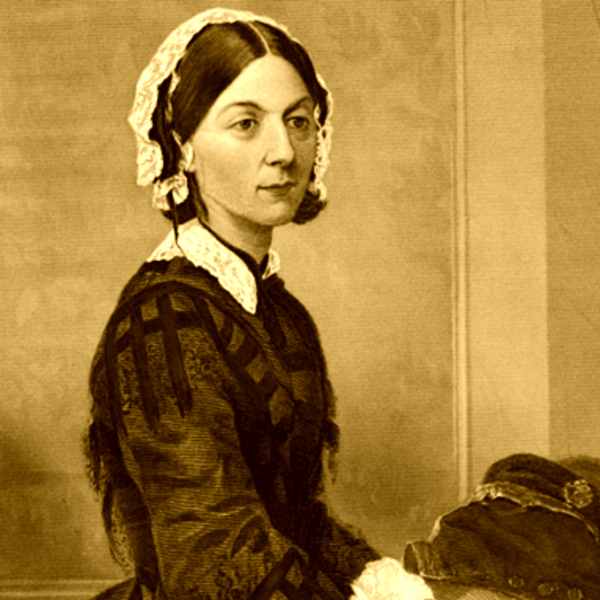
Florence Nightingale, pioneira da ciência na saúde Questão de Ciência
Lived 1820 - 1910. Immortalized as the lady with the lamp, Florence Nightingale was a highly intelligent, mathematically astute pioneer of better health outcomes. Her innovations resulted in lower death rates - first in hospitals, then in wider society. She formulated and implemented enormous reforms of nurse training and nursing practices.

Florence Nightingale, 1820 1910 Florence, later known as "The Lady With The Lamp", was born in
Florence Nightingale biography Introduction Famous for being the 'Lady with the Lamp' who organised the nursing of sick and wounded soldiers during the Crimean War, Florence Nightingale's far-sighted ideas and reforms have influenced the very nature of modern healthcare. Her greatest achievement was to transform nursing into a respectable profession for women

Celebrando Florence Nightingale a menina que seguiu seu instinto e revolucionou a medicina
Florence Nightingale was a trailblazing figure in nursing who greatly affected 19th- and 20th-century policies around proper medical care. She was known for her night rounds to aid the wounded.
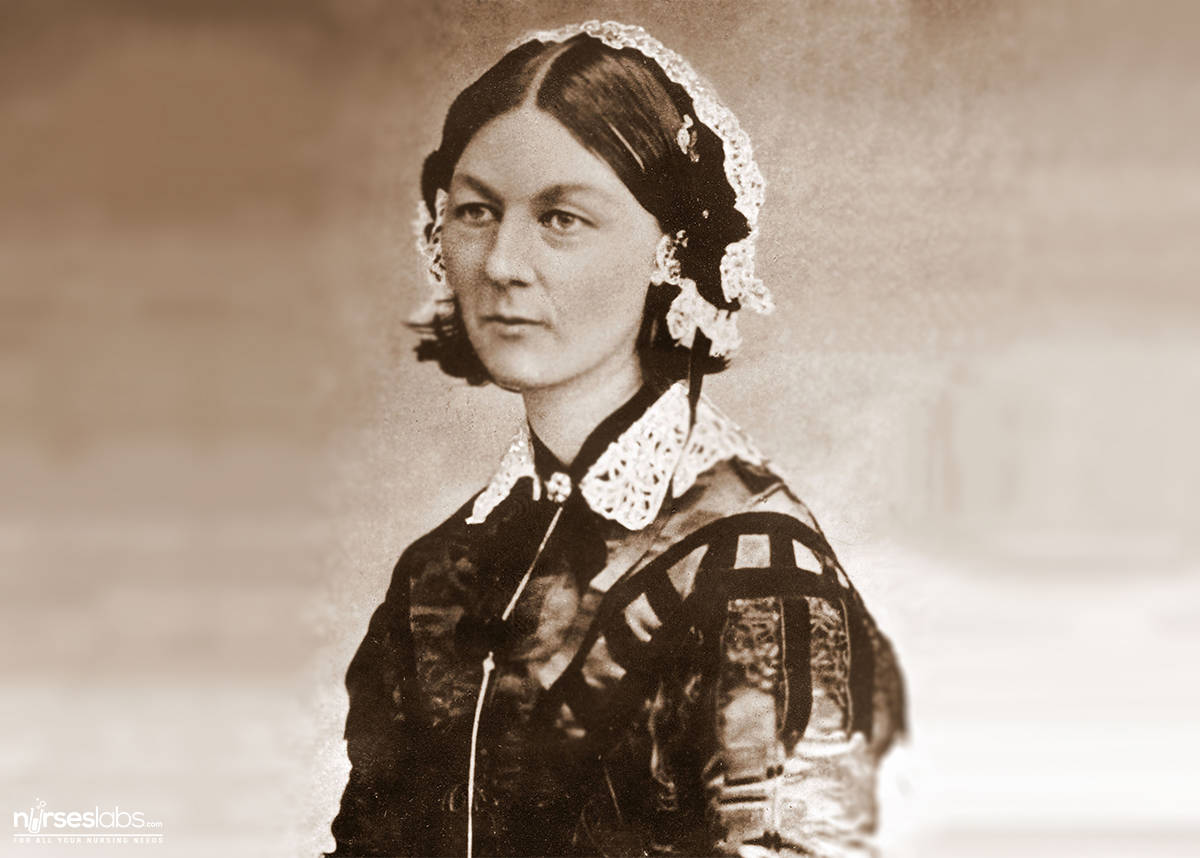
Florence Nightingale Biography and Works Nurseslabs
Florence Nightingale, OM, (Firenze, Toszkánai Nagyhercegség, 1820. május 12. - London, Egyesült Királyság, 1910. augusztus 13.) angol ápolónő és statisztikus. A modern nővérképzés, valamint a betegellátás reformjának elindítója. Ő alkalmazott először statisztikai megközelítést a betegápolás hatékonyságának elemzésére, így a bizonyítékokon alapuló orvoslás.